Invited Speakers
Pascal Lorenz
Professor, University of Haute-Alsace, France, FranceSpeech Title: Advanced architectures of Next Generation Wireless Networks
Abstract: Internet Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms are expected to enable wide spread use of real time services. New standards and new communication architectures allowing guaranteed QoS services are now developed. We will cover the issues of QoS provisioning in heterogeneous networks, Internet access over 5G networks and discusses most emerging technologies in the area of networks and telecommunications such as IoT, SDN, Edge Computing and MEC networking. We will also present routing, security, baseline architectures of the inter-networking protocols and end-to-end traffic management issues.
Fusaomi Nagata
Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Sanyo-Onoda City University, JapanSpeech Title: Pixel-Based Visual Feedback Controller for an Articulated Robot on a Sliding Rail
Abstract: The authors have developed a CNN&SVM design and training tool for defect detection of resin molded articles, and the usefulness and validity have been proved through several design, training and evaluation experiment of CNNs and SVMs [1]. The tool further enables to easily design powerful CNN models based on transfer learning concept, so that a pick and place robot with a visual feedback controller and transfer learning-based CNN models is introduced [2]. The visual feedback controller enabled to omit the complicated calibration between image and robot coordinate systems, also the transfer learning-based CNNs allowed the robot to estimate the orientation of target objects.
In this paper, a CNN acquired by transfer learning of AlexNet, which was already trained using about 1.2 million images of 1000 categories in ImageNet database, is introduced to recognize the orientations of objects. The original AlexNet is able to classify input images into one of 1,000 kinds of objects, while the transferred CNN is able to recognize the orientation of an object in images with the resolution of 15 degrees. Then, a pixel-based visual feedback control is designed and implemented into an articulated robot so that the gripper of the pick and place robot can automatically move to the position nearly just above a target object. Furthermore, a sliding rail is considered to allow the articulated robot to move around in wider working range. The visual feedback controller was extended to utilize the sliding rail. The usefulness and validity of the robot system using the sliding rail is confirmed through pick and place experiments of randomly put objects on a table.
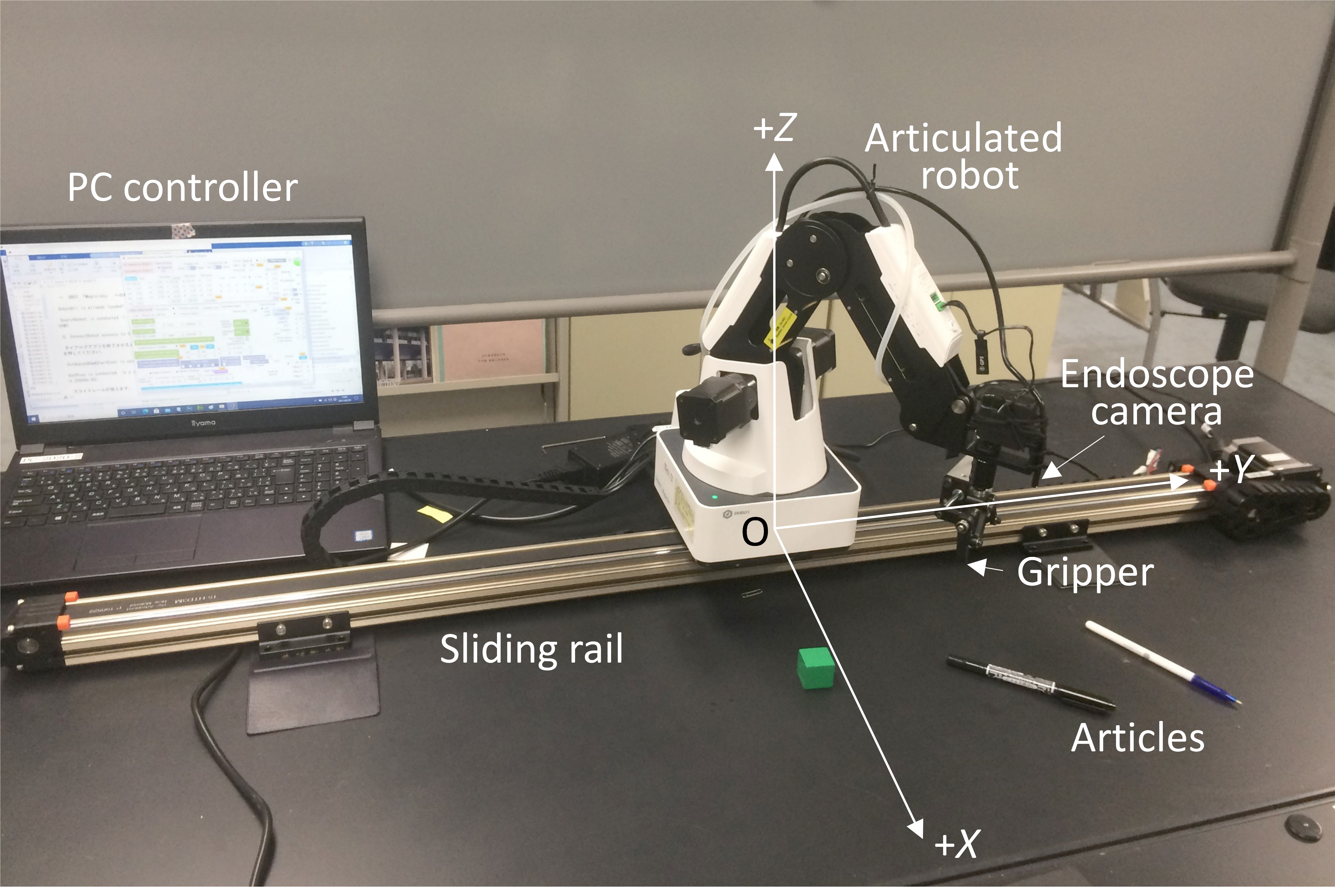
Figure 1 Extended picking robot using a sliding rail.
[1] K. Nakashima, F. Nagata, H. Ochi, A. Otsuka, T. Ikeda, K. Watanabe, M.K. Habib, Detection of Minute Defects Using Transfer Learning-Based CNN Models, Artificial Life and Robotics, Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 35-41, Springer, 2021.
[2] K. Miki, F. Nagata, K. Watanabe, M.K. Habib, Picking Robot of Defective Molded Articles Using Image Processing Technique and Visual Feedback Control, Procs. of 26th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics (AROB 26th 2021), pp. 498-502, 2021.
Keywords: Pick and place robot, Sliding rail, Convolutional neural network, Transfer learning, Visual feedback control
Henry Hexmoor
Professor, School of Computing, Southern Illinois University, USASpeech Title: The Democratic Appeal of Blockchain for the Internet of Everything
Abstract: Blockchain offer the possibility of a pair of strangers to directly and securely perform a variety of transactions to trade over all types of goods, information, and services without reliance on the traditional trust authorities such as legal and financial institutions. Blockchain provides a distributed digital record that does not require trust or coordination between firms, allowing for secure, and standardized transactions. All records on the blockchain are cryptographically hashed and transactions are signed by participants so that all user interactions on cloud platforms are confidential under blockchain enabled signatures. Blockchain interconnects and offers a fully decentralized storage without requiring a central authority. Digitized contracts, known as smart contracts, allow cryptographic access authentication and data sharing verification. Blockchain smart contracts identify, validate requests, and grant access permissions for users by triggering transactions or messages.
We will explore what the future holds for a variety of industry 4.0 applications mediated with the latest evolution of blockchain technology heralding an effective method for information sharing in a hyper-connected, decentralized and cloud empowered digital world.
We will discuss design and implementations for efficient security including consensus mechanism and end to end communication strategies as well as data privacy and security. We will highlight demand response energy management available for the consumption and trading of electric power data in the smart grid (i.e., the internet of energy), peer-to-peer energy trading, intelligent transportation and the internet of things.
We will sum up with the prospect and a siren call for the blockchain emergence as an instrument for democratization of the internet of everything avoiding that fragility of political democracy that can be slow and unfair.
Ding Wang
Associate Professor, School of Information Systems Engineering, Information Engineering University, ChinaSpeech Title: Research on key technologies of collaborative direct position determination of sea-aero targets based on distributed arrays
Abstract: High-precision positioning for high-value sea-aero targets (including ships, aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicle, etc.) has important practical significance. This report combines the direct-position-determination (DPD) technology with the collaborative processing idea, and focuses on the key technologies of collaborative DPD for sea-aero targets based on distributed arrays. Aiming at the characteristics of sea-aero target location scenario, this report proposes four kinds of collaborative processing methods, which include the methods making use of the modulation mode of the emitter signal; the methods utilizing the spatial correlation of target group; satellite-ground collaborative positioning methods; and the methods applying the measurement information from the calibration sources. For each kind of collaborative location methods, we construct the distributed array model and propose the collaborative DPD methods. Additionally, the location performance of the new methods is verified by simulation experiments. Theoretical and simulation results show that the collaborative DPD methods can significantly improve the positioning accuracy for sea-aero targets.
Keywords: Target positioning; Sea-aero target; direct-position-determination (DPD); Collaborative positioning
Nebojša Bačanin Džakula
Associate professor & Vice-Rector, Singidunum University, Belgrade, SerbiaSpeech Title: SWARM INTELLIGENCE APPLICATIONS IN CLOUD COMPUTING TASK SCHEDULING AND LOAD BALANCING
Abstract: Cloud computing paradigm, like the paradigm of network computing, is based on the clustering of resources and on the usage of network and Internet technologies. In general, the cloud computing refers to a new way of delivering computing resources in a form of service, such as data, software and hardware components (processing elements, memory and storage).
Cloud computing is a current and important multidisciplinary field, followed by a large number of published papers in the state-of-the-art international journals, as well as in the proceedings of the world-renowned international conferences. Based on the scientific results which have been gathered from the published papers in this domain, it can be concluded that there are many challenges and problems in the cloud environment, which can be more efficiently tackled by applying improved methods, techniques and algorithms. One of the most important challenges in cloud computing is scheduling of end users' requests on a limited set of available resources (virtual machines). A scheduling problem in cloud environment can be defined as an execution schedule of tasks on a limited set of available resources, taking into account the potential constraints and objective function.
Task scheduling is performed by scheduling algorithms, which can be divided into static and dynamic. In the case of a static scheduling, where it is not possible to dynamically switch tasks from over utilized to underutilized virtual machines, tasks are being allocated for execution on available virtual machines before the scheduling algorithm execution. In the case of the dynamic scheduling methods, which are known in the literature as load balancing approaches, a workload allocation between active virtual machines is being performed during the scheduling algorithm run-time. Requests' redistribution is executed by dynamically switching from over utilized to less utilized virtual machines. Heuristics and metaheuristics optimization methods are mostly used for dynamic scheduling, where they have achieved great results.
Task scheduling and load balancing problems in cloud computing belong to the group of NP hard combinatorial and/or global problems with or without constraints. Based on the published results in the relevant literature, it can be concluded that the swarm intelligence metaheuristics have been successfully tested on benchmark and practical NP hard optimization problems, and that they have achieved better results in terms of convergence speed and the solutions' quality, than other methods, techniques and algorithms. In our experiments, it is examined whether it is possible to further improve the task scheduling and load balancing in cloud computing environment by applying swarm intelligence metaheuristics.
During the experimental research, several swarm intelligence metaheuristics were improved and adapted for solving task scheduling and load balancing problems in cloud environment. Some of the swarm algorithms that proved state-of-the-art performance in terms of results’ quality, as well as of convergence speed are monarch butterfly optimization (MBO), whale optimization algorithms (WAO), elephant herding optimization (EHO), tree growth algorithm (TGA) and grey wolf optimization (GWO). The algorithms were implemented in both, original and modified/hybridized versions. The robust environment of CloudSim platform was utilized as the simulation platform.
In this speech, I will highlight the most significant results that the swarm algorithms obtained in the domain of cloud computing task scheduling and load balancing.
Noraziah Ahmad
Associate Professor, Faculty of Computing/Centre for Software Development & Integrated Computing, Universiti Malaysia Pahang, MalaysiaSpeech Title: Managing MyGRANTS Fragmented Database Using Binary Vote Assignment Grid Quorum with Association Rule (BVAGQ-AR) Replication Model
Abstract: Replication is one of the mechanisms managing data since it improves data access and reliability. Large amounts of data have been produced at a rapid rate since the invention of computers, especially during the pandemic scenarios. This condition is the key motivation for up-to-date and forthcoming research frontiers. However, in recent years, with widely available, low-cost technology, the amount of various data grows rapidly. The problem is although we are packed with data, but we have lacked of knowledge. Nevertheless, if the impractical data is used in database replication, this will cause waste of data storage and the time taken for a replication process will be delayed. This paper propose a new algorithm namely Binary Vote Assignment on Grid Quorum with Association Rule (BVAGQ-AR) in order to handle fragmented database replication. BVAGQ-AR algorithm is capable of partitioning the database into disjoint fragments. Fragmentation in distributed database is very useful in terms of usage, reliability and efficiency. Handling fragmented database replication becomes challenging issue to administrator since the distributed database is scattered into split replica partitions or fragments. We address how to build reliable system by using the proposed BVAGQ-AR algorithm for distributed database fragmentation by using Malaysian Greater Research Network (MyGRANTS) data as a case study. The result shows that managing fragmented database replication through proposed BVAGQ-AR algorithm able to preserve MyGRANTS data consistency.
Zhihan Lv
Associate Professor, Qingdao University, ChinaSpeech Title: An Optimized Byzantine Fault Tolerance Algorithm for Consortium Blockchain
Abstract: According to different application scenarios of blockchain system, it is generally divided into public chain, private chain and consortium chain. Consortium chain is a typical multi-center blockchain, because it has better landing, it is supported by more and more enterprises and governments. We analyze the advantages and problems of PBFT algorithm for the application scenarios of the consortium chain. In order to be more suitable for consortium chains, we propose a new optimized consensus algorithm based on PBFT. Aiming at the shortcomings of PBFT, such as the inability to dynamically join nodes, low multi-node consensus efficiency, and primary master node selection, our optimized algorithm has designed a hierarchical structure to increase scalability and improve consensus efficiency. The simulation results show that compared with PBFT and RAFT, our new consensus algorithm increases the data throughput while supporting more nodes, and effectively reducing the consensus delay and the number of communication times between nodes.
Yutaka Fukuchi
Associate Professor, Tokyo University of Science, JapanSpeech Title: Stable, wavelength-tunable and amplitude-equalized rational harmonic mode-locked laser employing a short bismuth-oxide-based highly nonlinear erbium-doped fiber
Abstract: Harmonically mode-locked fiber lasers (HMLFLs) have proven to be able to generate wavelength-tunable short pulses with small timing jitter and gigahertz repetition rates. Generally, the repetition rate of the HMLFLs given by nfcav is equal to the modulation frequency fmod of the intra-cavity modulator, where n is an integer called harmonic order, and fcav is the fundamental cavity frequency. Therefore, the maximum repetition rate is normally limited by the modulator bandwidth. Recently, a technique called rational harmonic mode locking has attracted considerable interest. In this technique, a pulse train with a repetition rate of (pn+1)fcav can be generated when fmod is set at (n+1/p)fcav, where p is an integer called rational harmonic order. However, the pulse amplitude becomes uneven when p is greater than two. Uneven amplitudes create difficulties in the real application. The wavelength tuning range is also another important issue of the HMLFLs. Furthermore, typical cavity length is 10-100 m, and n is 500-5000 for 10-GHz mode locking, which results in instability owing to the external perturbation and the large supermode noise. In this presentation, we review a rational HMLFL employing a short bismuth-oxide-based highly nonlinear erbium-doped fiber (Bi-HNL-EDF). Ultra-wide wavelength tunability covering both the C- and L-bands is achieved by utilizing a broadband gain profile of the Bi-HNL-EDF. The supermode noise is suppressed effectively due to a high nonlinearity of the Bi-HNL-EDF. The pulse-amplitude equalization is also achieved by a modulator transmittance adjustment method. The fiber cavity is as short as 6 m. Thus, stable and amplitude-equalized near-TL short pulses up to 40 GHz (p = 4) are successfully observed over the entire wavelength tuning range.
Keywords: Optical fiber lasers, mode-locked lasers, rare-earth materials, nonlinear optics, wavelength tuning, noise
Baochang Zhang
Professor, Beihang University, Beijing, ChinaSpeech Title: Visual Edge Computing and Depdendable Learning
Abstract: Visual edge computing become one of hottest topics in the field of artificial intelligence. Prof. Baochang Zhang will introduce their works including handcrafted models to deep models, especially focusing on binarized neural networks and neural architecture search. His HGPP and LDP methods are highly cited by more 1700 google citations. He provides the first attempt to consider the hidden relationship among variables in gradient descent, and introduce cogradient descent method to train neural networks more efficiently. Dr. zhang had achieved 3 International competition awards on ICPR2020 and ECCV2020 on object detection and classification.
Siti Barirah Ahmad Anas
Associate Professor, Department of Computer and Communication Systems Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, MalaysiaSpeech Title: Investigation of Backscattered Stimulated Raman Scattering in Optical Time Domain Reflectometer Active Monitoring
Abstract: The deployment of optical fibre for telecommunication network grows rapidly as it promises greater capacity of data transmission. Therefore, a good monitoring system is required to ensure that the optical fibre is in good condition and providing maximum service availability. Active fibre monitoring system has been developed based on optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) to overcome the limitation of its passive monitoring counterpart. A monitoring wavelength of 1625/1650 nm are normally deployed apart from the wavelengths used for data traffic transmission. Active fibre monitoring provides real-time monitoring so that any failure will results in faster restoration. However, the utilization of both traffic and OTDR in the wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) system will affect the dynamic range of the OTDR caused by backscattered stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This study implemented a software simulation model and hardware experimentation to investigate and mitigate the backscattered SRS signal in OTDR active fibre monitoring using 1650 nm wavelength. The investigation was carried out by developing basic OTDR active fibre monitoring system to observe the SRS backscattered noise, power depletion, and amplification using software simulation. The obtained results indicate that the booster amplifier link contributes the highest backscattered SRS including amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) noise. The simulation setup was also used to mitigate the backscattered SRS by placing a chirped fibre Bragg grating (CFBG) at the OTDR to allow only 1650 nm OTDR signal to be received by the OTDR leaving other unwanted signal or noise behind. This mitigation successfully reduces other backscattered signals approximately by 4 dB. Finally, a proof-of-concept hardware experiment is developed to test the feasibility of the proposed technique. The result shows that the OTDR trace for booster amplifier setup was distorted with OTDR penalty of 3.4 dB due to the backscattered noise. By mitigating the backscattered noise, the distortion in the trace was reduced and the OTDR penalty also reduced to 0.41 dB. Hence, coupling an OTDR into a WDM system requires an additional filter to suppress the backscattered noise, and subsequently improving the OTDR active fibre monitoring performance.
Keywords: Backscattered SRS, OTDR active monitoring, point-to-point transmission, optical access networks.
Acknowledgements: This work is funded by Fundamental Research Grant (FRGS), Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, No. FRGS/1/2020/TK0/UPM/02/10. The authors would also like to thank TMR&D and Kumpulan ABEX Sdn. Bhd. in providing the facilities for hardware experimentation.
Gyu Myoung Lee
Professor, Liverpool John Moores University, UKSpeech Title: Challenges for trust in IoT and AI
Abstract: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) are very important technologies for the future and there are a lot of research activities to combine AI and IoT, called AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things). Furthermore, data is becoming essential to support AI based solutions with human interactions. In this regard, this talk introduces key concepts, features and characteristics of human centric AIoT in data driven networking point of view. From AIoT research, many researchers have identified that there are security, privacy and trust concerns to realize human-centric AIoT. To cope with negative effects of AIoT, it's necessary to address trustworthy AIoT. Therefore, this talk presents key challenges for realizing trustworthy AIoT and discuss next steps for future research.
Miroslav Joler
Professor, University of Rijeka, CroatiaSpeech Title: On Characterization of Dielectric Properties of Non-standard Materials Using a Low-cost Resonator Circuit
Abstract: In design of wearable electronics, engineers face a task of having to sufficiently accurately determine dielectric properties of non-standard substrate materials, such as various fabrics, in order to successfully design a desired circuit, e.g. a textile antenna or a substrate-integrated waveguide. It is known that determination of dielectric properties is a subtle task, even nowadays, when sophisticated hardware and software are available, due to sensitivity of the measurement on various factors that are involved in the process. Depending on the type of the material sample to be characterized, several measurement methods are widely known, each with distinctive traits. It turns out, however, that even the most advanced and costly measurement apparatuses today can offer only a modest accuracy, followed by disclaimers regarding the measurements conditions. Given that fact, a viable alternative can be to design our own, low-cost, measurement setup that could provide a satisfactory accuracy for practical purposes. One such approach is based on the resonator circuit. Although the topic has been tackled in various papers, one will hardly find a complete or transparent and detailed measurement procedure that is part of the public domain, which cognition spontaneously lead us to revisit the topic. In this talk, an overview of the measurement principle of a ring resonator structure will be introduced and some previously defined approaches commented on. Dependence of the results on the characteristics of the sample and the resonator will be discussed based on full-wave numerical solver simulations and measurements. Finally, a hybrid approach, as a combination of an analytical model and sample measurement, will be presented for determination of relative permittivity and loss tangent of a material sample.
Rajkumar Soundrapandiyan
Associate Professor, School of Computer Science and Engineering, VIT University, IndiaSpeech Title: An approach for infrared image pedestrian classification based on local directional pixel structure elements’ descriptor
Abstract: Pedestrian classification is a major problem in infrared (IR) images due to lack of shape, low signal-to-noise ratio and complex background. And it find applications in agriculture, forestry, night vision monitoring system, intelligence system and defence system. In this paper, local directional pixel structure elements descriptor (LDPSED)-based pedestrian classification approach is proposed to overcome these problems. In addition, for segment the objects (pedestrian and non-pedestrian) from an IR image interest point detection approach is proposed. The proposed method consists of three steps segmentation, feature extraction and classification. Firstly, objects are segmented from the input image. Secondly, the feature extraction is carried out on the segmented objects. Finally, support vector machine (SVM) is implemented for classification of objects in IR image into pedestrian and non-pedestrian. To prove the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we have conducted experimental test on the standard OTCBVS-BENCH-thermal collection over the OSU thermal pedestrian database. In addition, the classification results of the proposed approach are compared with the existing approaches. The efficiency of the proposed approach is proven by high classification accuracy.
Keywords: infrared image; local directional pattern; structure element descriptor; support vector machine; pedestrian classification.
Tatjana Sibalija
Professor, Belgrade Metropolitan University, SerbiaSpeech Title: Parametric Optimization of Integrated Circuit Assembly Process: an Evolutionary Computing-Based Approach
Abstract: Strict demands for very tight tolerances and increasing complexity in the semiconductors’ assembly impose a need for an accurate parametric design that deals with multiple conflicting requirements. This paper presents application of the advanced optimization methodology, based on evolutionary algorithms (EAs), on two studies addressing parametric optimization of the wire bonding process in the semiconductors’ assembly. The methodology involves statistical pre-processing of the experimental data, followed by an accurate process modeling by artificial neural networks (ANNs). Using the neural model, the process parameters are optimized by four metaheuristics: the two most commonly used algorithms - genetic algorithm (GA) and simulated annealing (SA), and the two newly designed algorithms that have been rarely utilized in semiconductor assembly optimizations -teachinglearning based optimization (TLBO) and Jaya algorithm. The four algorithm performances in two wire bonding studies are benchmarked, considering the accuracy of the obtained solutions and the convergence rate. In addition, influence of the algorithm hyper-parameters on the algorithms effectiveness is rigorously discussed, and the directions for the algorithm selection and settings are suggested.
Tadeusz Czachorski
Professor, Institute of Theoretical and Applied Informatics, Polish Academy of Sciences, PolandSpeech Title: Modelling and Performance Evaluation of Packet Aggregation Mechanisms
Abstract: Packet aggregation is a valuable strategy to increase throughput, improve resource utilisation, and reduce energy consumption in access networks, high-speed Internet core networks, and cloud computing data centre networks.
The recent increase in the amounts of small packets generated by IoT networks, wireless sensor networks, and 4G/5G mobile networks has increased the need for more research on how to efficiently implement packet aggregation to meet the specific needs of these networks. The major drawback of packet aggregation mechanisms is the significant amount of delay that it introduces, making it unsuitable for packets that belong to real-time applications. The article presents a detailed review of packet aggregation applications in access networks (IoT and 4G/5G mobile networks), optical core networks, and cloud computing data centre networks.
Then we propose analytical models for evaluating the performance of packet aggregation mechanisms. They are based on diffusion approximation, where the diffusion process represents the increasing with time content of the aggregation buffer, periodically emptied following aggregation strategy. This approach allows us to consider time-dependent queueing models with time varying input flows, with general interarrival and service time distributions. The models may be fitted to any distribution of the size of aggregated and resulting packets.
Therefore they are are more general than others models presented till now.
The presented numerical examples refer to the N-GREEN (Next Generation of Routers for Energy Efficiency Networks), where smaller electronic packets called Service Data Units (SDUs) from access networks (e.g., DSL, wired and wireless LANs, 2G/3G/4G/5G mobile networks, and IoT networks), are stored following a First-in-First-out (FIFO) queueing discipline. At every time slot allocated to the buffer, the SDUs are aggregated into larger packets called Packet Data Units (PDUs) of the fixed size that are converted into optical packets and then inserted into the optical transmission system, provided that the optical transmission channel is not occupied.
Maltsev Alexander
Professor, Mobile Communications Department, University of Nizhny Novgorod (UNN), RussiaSpeech Title: Phase Tracking Sequences for 5G NR in 52.6-71 GHz Band: Design and Analysis
Abstract: This paper presents a novel approach to the phase tracking reference signal (PTRS) design in the 5G NR communication systems intended to work in a new 52.6 GHz to 71 GHz frequency band. For detailed problem illustration, the phase noise (PN) compensation algorithms are discussed and explained, from the basic common phase error (CPE) compensation to the MMSE-based inter carrier interference (ICI) filtering in frequency domain. Performance of the different algorithms is investigated for the baseline PTRS structure accepted in the current 5G NR specification and compared with a new proposed approach to the PTRS design. This approach is based on nulling a few subcarriers adjacent to each reference signal to minimize influence of the ICI on the PN estimation process. It was shown that the new PTRS design outperforms currently used distributed PTRS structure. Moreover, with new PTRSs, the performance of the simple least squares (LS) phase noise estimation method reaches the performance of the semi-optimal MMSE estimator, which has significantly larger complexity. Generally, achievable level of phase noise compensation for a given PTRS overhead is determined by the filter size, while advanced algorithms and approaches may improve filter coefficient estimation accuracy.
Keywords: 5G NR, phase tracking, phase noise, PTRS, common phase error, OFDM, least squares, phase noise compensation
Acknowledgements: Authors deeply thank Dr. Woong-Kee Min from the LG Technology Center, Moscow and Dr. Joon-Kui Ahn from the LG Electronics, Seoul for the organization of fruitful cooperation between overseas teams and making this paper possible
Sudan Jha
Professor and RAC member at the School of Sciences, Christ (Deemed to be University) Delhi, IndiaSpeech Title: Multi-RAT orchestration method for heterogeneous wireless networks
Abstract: Orchestration of multiRAT heterogeneous networks is not a trivial task. Implementation of such a solution in real network situations requires the use of continuously reported indicator values, which are measured and/or estimated in either terminal or at a network element. The appropriate decision-making algorithm and process also need to be deployed. The use of too simple algorithms may lead to, e.g., frequent path switching or selecting not appropriate RAN from an energy efficiency (or other) perspective. Interesting approach, also in terms of research, could be the use of Artificial Intelligence algorithms and machine learning techniques to build a self-learning self-organizing decision making module in the orchestrator based on historical data from a given geographical area and period of time but in some cases it may also not provide an optimal solution. The presented solution would support also all other types of network solutions (e.g., LoRa, Sigfox, Zigbee, Bluetooth, and others) also with different decision rules (not only Energy Efficiency but also e.g., Spectrum Efficiency, Relaying Time or others). It should be pointed out that the end-to-end orchestrator may support new operator-defined decision rules, also those based on business case rules, in contrast to the technical related QoS mentioned above. That approach would allow for the optimization of, e.g., operational costs, energy consumption, or setting time for operation of the network. Another aspect of such end-to-end multiRAT orchestration deployment could be security-related applications where parallel orchestrated transmission in different types of RAT networks can increase the level of security.
Therefore, the approach to wireless traffic steering in mobile networks can also be presented within to the high-level multi-RAT heterogonous network orchestration approach. Based on the high level network orchestrator which traces network indicators, it is possible to decrease user mobile terminal energy consumption keeping adequate traffic speed. The solution that will be discussed will be based on implementation in a testbed where Software Defined Radio is used. Downlink and Uplink data paths are toggled among different Radio Access Technologies according to the decisions which are taken by the developed End-To-End orchestrator based on received proper network traffic-related indicators.
Mahua Bhattacharya
Professor, Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management, IndiaSpeech Title: Role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in diagnostic procedure for efficient health care system
Abstract: Technologies based on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are having great role for de-cision support system of health care program in terms of efficacy and robustness. AI based tech-niques are quite capable of handling huge data for processing and analysis which brings speedy response to the endusers. Enormous volume of medical data acquired from various observations and technical processes needs AI and ML based technology to determine appropriate diagnostic procedure. In present day research medical data in macro, micro and nano or molecular levels are required to be processed and analyzed for interpretation of disease identification, prognosis and tendency of growth of any abnormal lesion. Various technical studies based on clinical symptoms and features lead to develop prediction model for therapeutic planning and drug delivery. In all these aspects accuracy in establishing correlation and coordination of features with medical ob-servation is a challenging task. The knowledge of information technology and computer engineer-ing are now taking care of these issues for a robust technical view to automate the diagnostic methods, analysis of immunology and treatment processes. Such techniques are successfully us-ing modern day AI and machine learning for an assistance to the conventional procedures of treatment planning. Present talk is aiming to address how a computer aided system may be de-signed based on AI and ML for an advanced diagnostic planning and treatment procedure.
Amrita Ruperee
Associate Professor & Dean- Students Activities, VCET, University of Mumbai, IndiaSpeech Title: Role of Massive MIMO and Next Generation Network
Abstract: Massive MIMO is an integral part of the next generation network. The pilot contamination is the major issue in Massive MIMO. We will cover Pilot contamination, the interference caused by reuse of the pilot signals to accommodate large number of users. It’s effect on the overall performance of the wireless network and Asynchronous pilot transmission with pilot hopping technique to enhance the data rate both for uplink and downlink with MMSE channel estimation in the presence of pilot contamination.
Diogo Lima
Professor, Universidade Paulista, BrazilSpeech Title: An approach of IoT enabled by TCNet: Trellis Code Network – a new algorithm and routing protocol
Abstract: This work proposes a new scenario that changes conventional paradigms to enable the development of QoS-aware protocols in WSNs, an important Infrastructure for the IoT architecture, using the new concept of “Trellis Coded Network”- (TCNet). The model is based on finite automata or Finite State Machines (FSM). The Low complexity of Finite State Machine (FSM) network nodes (“XOR” gates and shift registers), eliminating the use of any routing tables by means of Trellis decoding allowing to demonstrate the potential applications of the TCnet algorithm in some cases as Sensor Network Virtualization (VSN) and scenarios where clusters of nodes to allows cover large areas of interest where the sensors are distributed.
Harlisya Harun
Associate Professor, Satellite Communication and Avionics System Integration, Research Lab, Universiti Kuala Lumpur, MalaysiaSpeech Title: Analysis of the Characteristics of Space-time Trellis Code Generator Matrix Generated from Lisya Tree Structure
Abstract: The motivation behind space-time trellis code (STTC) is that STTC could fully utilise transmit diversity schemes that could reduce multipath fading in the multiantenna systems. The STTC encoding architecture which is the combination of the coefficients in the generator matrix G, provides an extension to the traditional trellis codes to multiantenna systems. Generator matrix G define the quality of STTC transmission, such that an optimal STTC (i.e full diversity and high coding gain) could be obtained through generator matrix G code search procedure. Thus, it is imperative to study the characteristics of generator matrices G, and to compare the performance of BER curves against SNR. A hundred of 16-minimum determinant (MD) generator matrices were generated from Lisya tree structure. The taxonomy of the generator matrices G was developed based on their isomorphism behaviour, which is classified into three main group namely reachable, non-reachable and fluctuated optimizations. Out of one hundred generator matrices sample, 24 percent of generic generator matrices performs the reachable characteristic, 50 percent for non-reachable characteristic and the rest were defined as fluctuated due to uncertainty of graph.
Tsuyoshi Minami
Professor, Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, JapanSpeech Title: Chemical Sensors Based on Water-Gated Organic Thin-Film Transistors
Abstract: Compact chemical sensors are in high demand for on-site detection of targets in aqueous media. Water-gated organic thin-film transistors (WG-OTFTs) fabricated by a simple procedure are among the most promising candidates for such sensors owing to their advantages. Especially, WG-OTFTs can be operated at an ultralow voltage (<1 V) that avoids undesirable electrochemical reactions. Hence, this speaker has developed WG-OTFT-based sensors using a chemical stimulus-responsive polymer, for which the changes in the electric double layer capacitance (EDLC) by accumulation and desorption of charged species are a key sensing mechanism. The speaker believes that the sensing strategy developed here based on WG-PTFTs can contribute to improving the quality of life in real-world scenarios.
Keywords: organic field-effct transistors, water, sensor
Rohini Deshpande
School of Electronics and Communication Engineering, REVA UNIVERSITY, IndiaSpeech Title:
Uyen T. Nguyen
Associate Professor, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University, CanadaSpeech Title:
SHASHI Mehrotra
Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, KL University, IndiaSpeech Title:
Roman Volianskyi
Associate Professor, Electrical Engineering Department, Dniprovsk State Technical University, UkraineSpeech Title:
Jerry Gao
Professor and Research Center Director, Computer Engineering Department, San Jose State University, USA;Applied Data Analytics Department, San Jose State University, USA
Speech Title: Intelligent Testing and Automation for Smart Autonomous Vehicles



























